Zarządzanie stanem aplikacji w oparciu o Redux w Angular
Zarządzanie stanem aplikacji w oparciu o Redux w Angular
Redux to kontener stanu aplikacji i implementacja popularnej architektury Flux (z ang. strumień, przepływ). Cały stan aplikacji przechowywany jest w jednym miejscu tzw. magazynie który z kolei jest jedynym źródłem prawdy o stanie aplikacji. Architektura Flux zakłada przepływ danych tylko w jednym kierunku. Zmiana stanu magazynu (z ang. store) możliwa jest tylko i wyłącznie za pomocą odpowiednich metod tzw. akcji przesyłanych do tzw. dispatchera który odpowiada za ich wykonywanie a tym zmianę stanu magazynu. Akcją może być np. kliknięcie przycisku przez użytkownika z GUI systemu. Utwórzmy prosta aplikację korzystającą z Reduxa. Na początek potrzebujemy mieć możliwość pobierania danych z Rest API.
Aby uprościć przykład nie będziemy projektować Rest Api tylko skorzystamy z gotowego rozwiązania jakim jest JSON Server. Jest to rozwiązanie które na podstawie zdefiniowanego pliku w formacie *.json pozwoli na wykonywanie zapytań restowych.
Tworzymy nowy projekt Angulara za pomocą Angular CLI oraz wykonujemy komendę:
json-server --watch customers.json
gdzie customers.json:
{ "customers": [ { "id": 1, "name": "Alice"}, { "id": 2, "name": "Tom"} ] }
Po uruchomieniu mamy dostęp do API pod adresem:
http://localhost:3000/customers
Zacznijmy od zdefiniowania serwisu odpowiedzialnego za pobranie danych z Rest API:
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core'; import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http'; import { catchError } from 'rxjs/operators'; import { throwError } from 'rxjs'; import { headers } from '../headers/headers'; @Injectable({ providedIn: 'root' }) export class CustomerService { constructor(private http: HttpClient) { } getAPICustomers() { return this.http.get('http://localhost:3000/customers', { headers }) .pipe(catchError((error: any) => throwError(error.message))); } }
Zdefiniujmy nagłówek informujący o typie przesyłanych danych:
import { HttpHeaders } from '@angular/common/http'; export const headers = new HttpHeaders().set('Content-Type', 'application/json');
- zdefiniujmy prosty model klienta:
export class Customer { name = ''; }
- Zdefiniujmy efekt:
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core'; import { Actions, Effect, ofType } from '@ngrx/effects'; import { switchMap, catchError, map } from 'rxjs/operators'; import { of } from 'rxjs'; import { CustomerService } from '../services/customerService'; import { getCustomerActionSuccess } from '../store/action/customer.actions'; import { getAPICustomers } from '../store/action/customer.actions'; import { Customer } from '../../models/customer'; @Injectable() export class CustomerEffects { constructor( private actions: Actions, private customerService: CustomerService ) { } @Effect() getAPICustomers = this.actions.pipe( ofType('getAPICustomers'), switchMap(() => this.customerService.getAPICustomers().pipe( map((customers: Array<Customer>) => getCustomerActionSuccess(customers)) ) ) ); }
Wszystkie asynchroniczne operacje oddelegowane są do efektów. Po wykonaniu operacji efekt zwraca akcje która przekazywana jest do reducera w celu zmiany stanu aplikacji.
- Zdefiniujmy akcje – mechanizm który zmienia stan aplikacji:
import { createAction, props } from '@ngrx/store'; import { Customer } from '../../../models/customer'; import { Action } from '@ngrx/store'; export const addCustomer = createAction( '[Customer] Add Customer', (customer: Customer) => ({customer}) ); export const clearCustomersStore = createAction( '[Customer] Clear Customer store', () => ({}) ); export const getCustomerActionSuccess = createAction( '[Customer] Get Customer', (payload: Array<Customer>) => ({payload}) ); export class getAPICustomers implements Action { readonly type = 'getAPICustomers'; }
- Zdefiniujmy reducer czyli mechanizm który na podstawie akcji aktualizuje stan aplikacji:
import {Action, createReducer, on} from '@ngrx/store'; import * as CustomerActions from '../action/customer.actions'; import {Customer} from '../../../models/customer'; export const customerFeatureKey = 'customer'; export interface CustomerState { customers: Customer[]; } export const initialState: CustomerState = { customers: [], }; export const customerReducer = createReducer( initialState, on(CustomerActions.addCustomer, (state: CustomerState, {customer}) => ({...state, customers: [...state.customers, customer], })), on(CustomerActions.clearCustomersStore, (state: CustomerState, {}) => ({...state, customers: [], })), on(CustomerActions.getCustomerActionSuccess, (state: CustomerState, {payload}) => ({...state, customers : payload })) ); export function reducer(state: CustomerState | undefined, action: Action): any { return customerReducer(state, action); }
- Zdefiniujmy selektor – selektory odpowiadają za dostarczanie danych ze stanu aplikacji:
import {createFeatureSelector, createSelector} from '@ngrx/store'; import * as fromCustomer from '../reducer/customer.reducer'; export const selectCustomerState = createFeatureSelector<fromCustomer.CustomerState>( fromCustomer.customerFeatureKey, ); export const selectCustomers = createSelector( selectCustomerState, (state: fromCustomer.CustomerState) => state.customers );
zdefiniujmy komponenty:
- customer-view:
import {Component} from '@angular/core'; import {Observable} from 'rxjs'; import {Customer} from '../../models/customer'; import {select, Store} from '@ngrx/store'; import {selectCustomers} from '../store/selector/customer.selectors'; import {CustomerState} from '../store/reducer/customer.reducer'; @Component({ selector: 'app-customer-view', templateUrl: './customer-view.component.html', styleUrls: ['./customer-view.component.scss'] }) export class CustomerViewComponent { customers$: Observable<Customer[]>; constructor(private store: Store<CustomerState>) { this.customers$ = this.store.pipe(select(selectCustomers)); } }
widok dla komponentu customer-view:
<h4>List of Customers</h4> <div *ngFor="let customer of customers$ | async; let i=index"> <span >{{i+1}}.</span> {{customer.name}} </div>
- customer-add:
import {Component} from '@angular/core'; import {Customer} from '../../models/customer'; import {addCustomer} from '../store/action/customer.actions'; import {clearCustomersStore} from '../store/action/customer.actions'; import {CustomerState} from '../store/reducer/customer.reducer'; import {getCustomerActionSuccess } from '../store/action/customer.actions'; import {getAPICustomers } from '../store/action/customer.actions'; import {selectCustomers} from '../store/selector/customer.selectors'; import {select, Store} from '@ngrx/store'; import {Observable} from 'rxjs'; @Component({ selector: 'app-customer-add', templateUrl: './customer-add.component.html', styleUrls: ['./customer-add.component.scss'] }) export class CustomerAddComponent { readonly CLEAR = 0; readonly NO_CLEAR = 1; counter = 0; constructor(private store: Store<CustomerState>) { } addCustomer(customerName: string): void { if(this.counter == this.CLEAR) { this.store.dispatch(clearCustomersStore()); this.counter = this.NO_CLEAR; } console.log(this.counter); const customer = new Customer(); customer.name = customerName; this.store.dispatch(addCustomer(customer)); } readCustomersFromAPI(): void { this.store.dispatch(new getAPICustomers()); this.counter = this.CLEAR; } }
widok dla komponentu customer-add:
<h4>Add New Customer</h4> <input #box > <button (click)="addCustomer(box.value)">Add</button> <button (click)="readCustomersFromAPI()">getFromAPI</button>
Na koniec plik konfiguracyjny customer.module.ts:
import {NgModule} from '@angular/core'; import {CommonModule} from '@angular/common'; import {CustomerViewComponent} from './customer-view/customer-view.component'; import {CustomerAddComponent} from './customer-add/customer-add.component'; import {StoreModule} from '@ngrx/store'; import {customerFeatureKey,reducer} from './store/reducer/customer.reducer'; import { CustomerEffects } from './effects/customer.effect'; import { EffectsModule } from '@ngrx/effects'; import { HttpClientModule, HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http'; @NgModule({ declarations: [CustomerViewComponent, CustomerAddComponent], imports: [ HttpClientModule, CommonModule, StoreModule.forFeature(customerFeatureKey, reducer), EffectsModule.forRoot([]), EffectsModule.forFeature([CustomerEffects]) ], exports: [ CustomerViewComponent, CustomerAddComponent ] }) export class CustomerModule { }
oraz widok app.component.html:
<div style="text-align:center"> <h1> Welcome to {{ title }}! </h1> </div> <app-customer-view></app-customer-view> <app-customer-add></app-customer-add>
Testujemy aplikację:
dodanie nowego klienta:
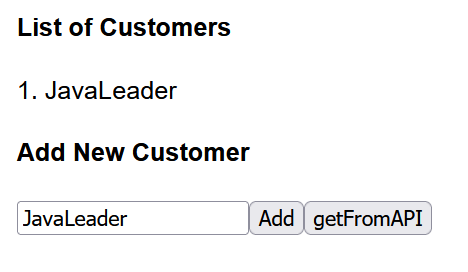
pobranie klientów z użyciem API (effects):
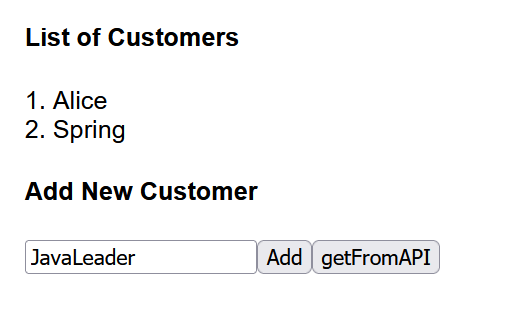
co dalej?
Można pokusić się o zaaplikowanie bazy danych klientów oraz zaprojektować operacje CRUD w Rest API.

Leave a comment